환경: spring batch 5.0.3, java 17
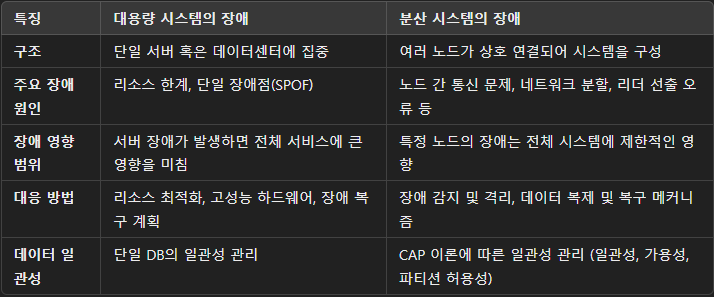
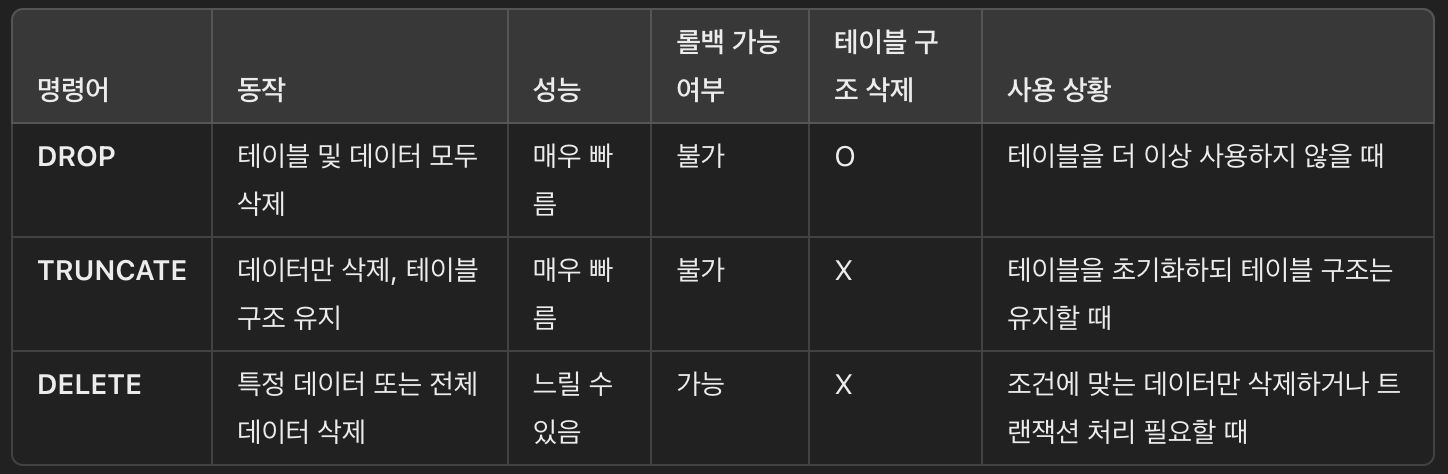
스프링 배치의 fault tolerant에는 크게 retry와 skip이 있다.
- skip(): ItemReader, ItemProcessor, ItemWriter 모두에서 예외 발생 시 적용할 수 있으며, 예외를 스킵하고 다음 아이템으로 넘어감
- retry(): ItemProcessor와 ItemWriter에만 적용되며, 예외 발생 시 설정된 횟수만큼 재시도. ItemReader에서는 retry()를 사용할 수 없음
- ItemReader의 read() 메서드는 한 번 호출될 때마다 단일 항목을 반환함. 만약 재시도하면 여러 번 호출해야 하며, 이는 ItemReader의 기본 설계 원칙에 맞지 않고 재시도는 데이터 읽기와는 별개의 책임이므로, ItemReader 내부에서 이를 처리하는 것은 설계 원칙에 어긋남
이번 글에서는 writer의 retry에 대해 집중해 본다.
에러로 인한 재시도를 하고 싶을 경우. faultTolerant()와 함께. retry()와. retryLimit() 설정을 사용하면 Spring Batch에서 Step 또는 Chunk 단위로 처리 중 발생하는 예외에 대해 재시도 처리를 할 수 있다.
private Step getCommonStep(
JobRepository jobRepository,
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager,
String stepName,
MyBatisCursorItemReader<GmahjongRankingRat> itemReader,
ItemWriter<GmahjongRankingRat> itemWriter) {
return new StepBuilder(stepName, jobRepository)
.listener(deleteAllBeforeStep)
.<GmahjongRankingRat, GmahjongRankingRat>chunk(CHUNK_SIZE, transactionManager)
.reader(itemReader)
.writer(itemWriter) ///-> 에러 발생
.faultTolerant()
.retry(RuntimeException.class)
.retryLimit(2) // -> 재시도 두번
.listener(retryListener())
.build();
}
1. .faultTolerant()
- Fault Tolerant Step을 설정
- Step이나 Chunk 처리 중 예외가 발생했을 때, 해당 예외를 허용하거나 재시도할 수 있도록 구성
- retry, skip, noRollback, noRetry 등의 다양한 옵션을 적용할 수 있는 시작점
2. .retry(Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionClass)
- 재시도 대상 예외 타입을 지정
- 예외 타입은 특정 예외 클래스(예: RuntimeException.class) 또는 그 하위 클래스
예를 들어, .retry(RuntimeException.class)를 설정하면 RuntimeException과 그 하위 클래스에서 예외가 발생할 때마다 재시도가 이루어짐
3. .retryLimit(int retryLimit)
- 최대 재시도 횟수를 설정
- retryLimit 값은 예외가 발생했을 때 최대 재시도 가능 횟수를 의미(총 횟수가 아닌 재시도 횟수)
- 예를 들어, retryLimit(2)로 설정하면 최대 2번 재시도함
- retryLimit에 설정된 횟수는 최초 시도에는 영향을 주지 않으며, 최초 시도 후 추가로 재시도할 수 있는 횟수를 의미
4. .faultTolerant().retry(RuntimeException.class).retryLimit(2)의 의미
- faultTolerant():
- 예외가 발생했을 때, 예외를 처리하거나 재시도할 수 있는 내구성 있는 단계로 설정
- 재시도 대상 예외 설정 (retry(RuntimeException.class)):
- RuntimeException과 그 하위 클래스에서 예외가 발생했을 때 재시도하도록 설정
- 최대 재시도 횟수 설정 (retryLimit(2)):
- 최초 시도 외에 최대 2번의 재시도를 허용
- 즉, 총 3번의 시도(초기 시도 1번 + 재시도 2번) <<<<<< 3일간 나를 고민에 빠트린 오늘의 주제...
재시도 테스트를 위해 3번 실행까지 에러를 발생시킨다.
@Bean
@StepScope
public ItemWriter<GmahjongRankingRat> insertTotalRank(
@Qualifier(DataSourceConfig.SESSION_FACTORY) SqlSessionFactory casualDb) {
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>> insertTotalRank");
return new ItemWriter<RankingRat>() {
private final SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate = new SqlSessionTemplate(casualDb);
private int attempt = 0;
@Override
public void write(Chunk<? extends RankingRat> items) {
attempt++;
System.out.println("Attempt " + attempt + ": Writing items " + items);
if (attempt < 3) { // 2번 이하로는 예외 발생
throw new RuntimeException("Intentional error on attempt " + attempt);
}
for (RankingRat item : items) {
sqlSessionTemplate.insert(
Constant.GAME_MAPPER + "insertTotalRank", item);
}
}
};
}
retry 할 때 로그를 보기 위해 retryListener도 만들어서 달아준다.
@Bean
public RetryListener retryListener() {
return new RetryListener() {
@Override
public <T, E extends Throwable> void onError(
RetryContext context, RetryCallback<T, E> callback, Throwable throwable) {
// 재시도 중 발생한 예외를 로깅
System.err.println(
"Retry attempt "
+ context.getRetryCount()
+ " failed with exception: "
+ throwable.getMessage());
}
};
}
예상 시나리오
최초 시도 -> 에러1 -> 재시도1 -> 에러2 -> 재시도2 -> 에러3 -> 재시도 횟수 2번이 지나서 종료처리
그래서 에러가 3번까지 발생하고, 재시도 로그 2번 남을 것이라 기대
10:54:24.210 [main] DEBUG o.s.b.c.s.i.FaultTolerantChunkProcessor - Attempting to write: ////최초 시도
10:54:24.221 [main] DEBUG o.s.batch.core.scope.StepScope - Creating object in scope=step, name=scopedTarget.insertTotalRank
>>>>>>>>> insertTotalRank
Attempt 1: Writing items... //최초 적재
...
10:54:24.247 [main] DEBUG o.s.b.core.step.tasklet.TaskletStep - Rollback for RuntimeException: java.lang.RuntimeException: Intentional error on attempt 1
10:54:24.247 [main] DEBUG o.s.t.support.TransactionTemplate - Initiating transaction rollback on application exception
java.lang.RuntimeException: Intentional error on attempt 1
...
10:54:24.250 [main] DEBUG c.a.i.imp.CompositeTransactionImp - rollback() done of transaction 10.78.130.172.tm172740206400000010
...
10:54:24.250 [main] DEBUG o.s.b.c.s.i.SimpleRetryExceptionHandler - Handled non-fatal exception
java.lang.RuntimeException: Intentional error on attempt 1
...
10:54:24.251 [main] DEBUG o.s.b.repeat.support.RepeatTemplate - Repeat operation about to start at count=2
...
Retry attempt 1 failed with exception: Intentional error on attempt 1
10:54:24.265 [main] DEBUG o.s.b.c.s.i.FaultTolerantChunkProcessor - Attempting to write: ////재시도 1
...
Attempt 2: Writing items... //재시도1 적재
10:54:24.282 [main] DEBUG o.s.b.core.step.tasklet.TaskletStep - Rollback for RuntimeException: java.lang.RuntimeException: Intentional error on attempt 2
10:54:24.282 [main] DEBUG o.s.t.support.TransactionTemplate - Initiating transaction rollback on application exception
java.lang.RuntimeException: Intentional error on attempt 2
...
10:54:24.282 [main] DEBUG c.a.i.imp.CompositeTransactionImp - rollback() done of transaction 10.78.130.172.tm172740206425100011
...
10:54:24.283 [main] DEBUG o.s.b.c.s.i.SimpleRetryExceptionHandler - Handled non-fatal exception
java.lang.RuntimeException: Intentional error on attempt 2
...
10:54:24.283 [main] DEBUG o.s.b.repeat.support.RepeatTemplate - Repeat operation about to start at count=3
10:54:24.288 [main] DEBUG o.s.b.c.s.i.FaultTolerantChunkProcessor - Attempting to write: ////재시도 2
...
Retry attempt 2 failed with exception: Intentional error on attempt 2
...
10:54:24.295 [main] DEBUG o.s.b.core.step.tasklet.TaskletStep - Rollback for RuntimeException: org.springframework.retry.ExhaustedRetryException: Retry exhausted after last attempt in recovery path, but exception is not skippable.
10:54:24.295 [main] DEBUG o.s.t.support.TransactionTemplate - Initiating transaction rollback on application exception
org.springframework.retry.ExhaustedRetryException: Retry exhausted after last attempt in recovery path, but exception is not skippable.
...
10:54:24.295 [main] DEBUG c.a.i.imp.CompositeTransactionImp - rollback() done of transaction 10.78.130.172.tm172740206428300012
...
10:54:24.298 [main] DEBUG o.s.b.repeat.support.RepeatTemplate - Handling fatal exception explicitly (rethrowing first of 1): org.springframework.retry.ExhaustedRetryException: Retry exhausted after last attempt in recovery path, but exception is not skippable.
10:54:24.299 [main] ERROR o.s.batch.core.step.AbstractStep - Encountered an error executing step gmahjongTotalRankingStep in job gmahjongDailyRankingJob
writer.write() 함수 두 번 호출됨. 3번째 시도를.. 하는 것 같긴 한데.. write 호출은 안 하고.. 횟수 초과로 전체 롤백을 하는 듯한 로그만 남음..
정확하게 세 번 시도를 하는 건지는 모르겠으나..(10:54:24.288과 10:54:24.295 사이에 실행 로그가 있어야 하지 않나)
"Rollback for RuntimeExceptioin", "rollback() done"의 로그가 세 번씩 남으므로 프로그램의 입장에선 에러를 세 번 감지한 것 같긴 하다..
참고로 rollback을 한다고 했지만 해당 chunk대한 부분만 rollback이라, beforeStep에서 한 deleteAll은 이미 적용되어 있고(테이블이 비어 있고) writer의 첫 chunk부터 에러 발생이라 결국 빈 테이블이 유지된다.
이 상태에서(retryLimit = 2; writer에서 첫 2번만 에러 발생)
retryLimit만 2 -> 3으로 올리면, 에러는 그대로 두 번, 총 시도는 최초 + 재시도 3번 = 4번이라 마지막에 성공해야 한다.
실행해보면, 위와 같은 에러가 두 번나고 마지막 쪽 로그가 아래처럼 바뀌면서 insert가 된다..
14:38:12 DEBUG [main] o.s.b.repeat.support.RepeatTemplate - Repeat operation about to start at count=3
14:38:12 DEBUG [main] o.s.b.c.s.i.FaultTolerantChunkProcessor - Attempting to write: ...
14:38:12 DEBUG [main] org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionUtils - Creating a new SqlSession
...// insert logs
뜻대로 되긴 하는데.. 아직도 왜 마지막 시도에 대한 로그가 제대로 안 찍혔는지 모르겠다.. write을 세 번 부르는 게 아닌가?
테스트 코드로 확인
@Test
void testRetryLimit() throws Exception {
// 첫 번째, 두 번째, 세 번째 호출에서 예외 발생
JobParameters jobParameters = getJobParameters();
given(totalRankingReader.read()).willReturn(userRats().get(0), userRats().get(1), null);
doNothing().doNothing().doNothing().when(deleteAllBeforeStep).beforeStep(any());
doAnswer(
invocation -> {
System.out.println("First write attempt");
throw new RuntimeException("error! 1");
})
.doAnswer(
invocation -> {
System.out.println("Second write attempt");
throw new RuntimeException("error! 2");
})
.doAnswer(
invocation -> {
System.out.println("Third write attempt");
throw new RuntimeException("error! 3");
})
.when(insertTotalRank)
.write(any(Chunk.class));
// Step 실행
JobExecution jobExecution =
jobTestUtils
.getJobTester(GmahjongRankingJobConfig.JOB_NAME)
.launchJob(jobTestUtils.makeJobParameters(jobParameters));
verify(totalRankingReader, times(3)).read();
// write 메서드가 총 3번 호출되었는지 확인
verify(insertTotalRank, times(3)).write(any(Chunk.class));
// Job이 실패했는지 확인 (최대 재시도 후 실패)
assertThat(jobExecution.getStatus()).isEqualTo(BatchStatus.FAILED);
}
retryLimit = 2 일 때 writer를 3번 부르는지 테스트 코드이다. 시도한 로그를 남기기 위해 doThrow가 아닌 doAnswer을 사용하였다.
위 테스트는 실패한다. 아래 부분에서 실제로 2번 호출했다고 검증된다.
verify(insertTotalRank, times(3)).write(any(Chunk.class));
관련 로그.. 본 로그와 크게 다르지 않다 세 번째 writer를 호출하는지 잘 모르겠는.. 로그다.
14:58:57.449 [Test worker] DEBUG o.s.b.c.s.i.FaultTolerantChunkProcessor - Attempting to write:
14:58:57.449 [Test worker] DEBUG o.s.retry.support.RetryTemplate - Retry: count=0
First write attempt
Retry attempt 1 failed with exception: error! 1
14:58:57.451 [Test worker] DEBUG o.s.retry.support.RetryTemplate - Checking for rethrow: count=1
14:58:57.459 [Test worker] DEBUG o.s.b.c.s.i.FaultTolerantChunkProcessor - Attempting to write:
14:58:57.460 [Test worker] DEBUG o.s.retry.support.RetryTemplate - Retry: count=1
Second write attempt
Retry attempt 2 failed with exception: error! 2
14:58:57.460 [Test worker] DEBUG o.s.retry.support.RetryTemplate - Checking for rethrow: count=2
14:58:57.466 [Test worker] DEBUG o.s.b.c.s.i.FaultTolerantChunkProcessor - Attempting to write:
14:58:57.466 [Test worker] DEBUG o.s.b.core.step.tasklet.TaskletStep - Rollback for RuntimeException: org.springframework.retry.ExhaustedRetryException: Retry exhausted after last attempt in recovery path, but exception is not skippable.
14:58:57.466 [Test worker] DEBUG o.s.t.support.TransactionTemplate - Initiating transaction rollback on application exception
파고들기..(w GPT)
1. retryLimit의 동작 원리
- retryLimit은 최대 재시도 가능 횟수를 의미합니다. 이는 "초기 시도 횟수를 제외한" 재시도 횟수입니다.
- 예를 들어, retryLimit = 2로 설정한 경우, 최초 시도 1번 + 재시도 2번 = 총 3번의 시도가 이루어집니다.
- 시도 1: 최초 시도
- 재시도 1: retryLimit에 의해 허용된 첫 번째 재시도
- 재시도 2: retryLimit에 의해 허용된 마지막 재시도
2. 로그 분석
2.1. 첫 번째 시도 (count=0)
- First write attempt 로그가 나타난 후 RuntimeException이 발생하여 재시도가 필요합니다.
- retry()가 적용되어 재시도 1이 시작됩니다.
2.2. 첫 번째 재시도 (count=1)
- Second write attempt 로그가 나타난 후 두 번째 예외가 발생합니다.
- retry()에 의해 마지막 재시도가 필요합니다.
2.3. 두 번째 재시도 (count=2)
- 이 시도에서도 실패하여 RetryTemplate의 ExhaustedRetryException이 발생합니다.
- 세 번째 재시도에서 예외 발생 후, 더 이상 재시도가 이루어지지 않습니다.
3. 실제 호출과 예외 발생 횟수 차이
위 로그에서 write() 메서드가 총 3번 호출된 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. 하지만 예외가 명시적으로 두 번만 발생하는 이유는 다음과 같습니다:
- 첫 번째 시도와 첫 번째 재시도: 첫 번째 시도와 첫 번째 재시도에서 예외가 발생하여 retry()가 작동했습니다. 이때 retryLimit에 따라 재시도가 시도됩니다.
- 두 번째 재시도: 두 번째 재시도에서 예외가 발생하면 retryLimit을 모두 소진하게 됩니다. 이 시점에서 ExhaustedRetryException이 발생합니다.
- 재시도 실패 후 처리: ExhaustedRetryException이 발생하면 더 이상 재시도가 이루어지지 않으며, 마지막 재시도 실패 후에는 예외가 발생한 상태로 처리됩니다.
4. ExhaustedRetryException의 의미
- ExhaustedRetryException은 설정된 재시도 한도(retryLimit)를 모두 소진한 후에도 예외가 해결되지 않았다는 의미입니다. 이 예외는 마지막 시도에서 예외가 발생했다는 것을 의미하며, 재시도가 더 이상 이루어지지 않음을 나타냅니다.
: 말이 애매하다. 총 3번의 시도를 하지만 writer를 부르는 시도는 아니고,, writer를 2번 부르고 재시도 횟수가 고갈되면 마지막 시도를 하기 전에 예외가 발생한다고 이해해야 할 것 같다.
참고로 첫 번째, 두 번째는 실패 세 번째에서 성공시키는 테스트 코드를 짜도 writer는 2번 불리고 전체 배치는 실패처리 된다.
최초 시도 -> 에러1 -> 재시도1 -> 에러2 -> 재시도2 -> 성공 -> ..전체 성공?이라고 생각하기 쉬운데..
이미 에러2에서 재시도 횟수(2)가 소비되어 에러가 발생하는 플로우다..
@Test
void testRetryLimit() throws Exception {
JobParameters jobParameters = getJobParameters();
given(totalRankingReader.read()).willReturn(userRats().get(0), userRats().get(1), null);
doNothing().doNothing().doNothing().when(deleteAllBeforeStep).beforeStep(any());
// 첫 번째, 두 번째 호출에서 예외 발생
doAnswer(
invocation -> {
System.out.println("First write attempt");
throw new RuntimeException("error! 1");
})
.doAnswer(
invocation -> {
System.out.println("Second write attempt");
throw new RuntimeException("error! 2");
})
.doNothing()
.when(insertTotalRank)
.write(any(Chunk.class));
// Step 실행
JobExecution jobExecution =
jobTestUtils
.getJobTester(GmahjongRankingJobConfig.JOB_NAME)
.launchJob(jobTestUtils.makeJobParameters(jobParameters));
verify(totalRankingReader, times(3)).read();
// write 메서드는 2번 호출
verify(insertTotalRank, times(2)).write(any(Chunk.class));
// Job이 실패했는지 확인 (최대 재시도 후 실패)
assertThat(jobExecution.getStatus()).isEqualTo(BatchStatus.FAILED);
흐름 설명:
- 첫 번째 시도 (Write attempt 1):
- write() 호출 → RuntimeException 발생 → 재시도 1로 진입.
- 첫 번째 재시도 (Write attempt 2):
- write() 호출 → 다시 RuntimeException 발생 → 재시도 2로 진입.
- 두 번째 재시도 (Write attempt 3):
- 결과 처리:
- 비록 세 번째 시도에서 성공했더라도, 재시도 한도인 retryLimit 2번을 모두 소진했으므로, 전체 Step이 실패로 처리됩니다.
- ExhaustedRetryException이 발생하여, 더 이상의 재시도 없이 실패로 간주됩니다.
재시도 한도 소진과 처리 방식
- 재시도 한도 소진:
- retryLimit에 따라 재시도 횟수가 소진되면 RetryTemplate은 더 이상 ItemWriter를 호출하지 않습니다.
- 재시도 중 실패한 예외를 처리할 수 없는 상태가 되면 ExhaustedRetryException을 발생시킵니다.
- 최종 예외 처리:
- 최종적으로 발생한 예외가 스킵 가능하지 않거나, 재시도 후에도 처리되지 않은 경우 전체 Step이 실패로 종료됩니다.
- 마지막 시도가 성공하더라도:
- 마지막 재시도에서 성공하더라도 재시도 한도가 모두 소진된 상태에서는 더 이상 재시도 없이 Step이 실패로 처리됩니다.
이.. 말싸움 때문에 3일 정도 매진한 것 같다..ㅠㅠ
결국, 재시도 횟수 차감되는 시점이 중요.....!