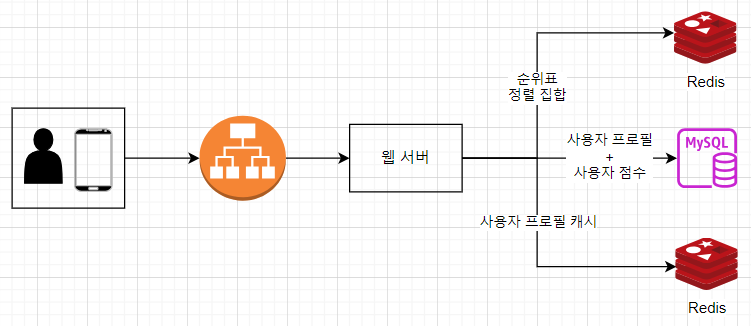
- 사용자는 모바일 앱에서 주변 친구를 확인
- 낮은 지연시간: 30초마다 갱신
- 결과적 일관성:
- 1억 DAU
- 동시접속 10% = 천만
- 30초마다 자기 위치를 시스템에 전홍
- QPS = 천만/30 = 334,000
- 로드밸런서: restful api서버, 양뱡향 유상태 ws서버 앞단에서 부하를 고르게 분산
- restful api 서버: 무상태, 친구 추가/삭제, 사용자 갱신 등
- ws 서버: 친구 위치 정보 전송, 커넥션 유지
- 기존 서버 제거 시 기존 연결을 종료하고 진행(LB에서 상태를 연결 종료 중으로 변경)
- 레디스 위치 정보 캐시: 최근 위치 캐시, ttl 설정 필요(갱신 혹은 비활성화)
- 사용자 아이디 - 위도/경도/시각 json
- 영속성 보장 필요 없음
- 메모리는 괜찮은데 QPS 감당하려면 캐시서버 샤딩 필요
- HA를 위해 복제
- 사용자 디비: 친구 관계 정보 저장(RDB, nosql)
- 사용자 상세정보; 친구 관계 데이터
- RDB사용 시 사용자 아이디 기준으로 샤딩
- 디비 직접 직의하지 말고 API 서버 호출
- 위치 이동 이력 디비: 사용자의 위치 변동 이력
- 사용자 아이디, 위도, 경도, 타임스탬프
- 막대한 쓰기 연산 부하를 감당하며 수평적 규모 확장 가능한 디비: 카산드라
- RDB사용할 경우 사용자 아이디를 기반으로 샤딩 필요..
- 레디스 펍/섭(메세지 버스): 채널(토픽)만드는 비용이 저렴; 위치 변경 메시지의 라우팅 계층
- 사용자의 위치가 변경되면 변경 이벤트를 발행하고 친구들이 구독하여 모든 친구의 웹소켓 연결 핸들러가 호출됨. 이벤트를 기반으로 검색 반경 등 계산 후 조건을 만족하면 친구의 앱으로 전송
- 채널을 유지하기 위해 구독자 관계를 추적하기 위한 해시 테이블과 연결 리스트가 필요한데 아주 소량의 메모리를 사용한다.
- 오프라인 사용자라 어떤 변경도 없는 채널의 경우 생성된 이후에 CPU자원은 전혀 사용하지 않는다.
- 주변 친구 기능을 이용하는 모든 사용자에게 채널 하나씩 부여
- 사용자는 초기화 시 친구 상태 상관없이 모든 친구와 구독 관계 설정
- 병목은 메모리가 아니라 CPU사용량
- 분산 레디스 펍섭 클러스터
- service discovery사용
- 해시 링에 활성화된 레디스 서버 보관

주기적 위치 갱신
- 위치 변경 사실을 LB에 전송
- LB는 변경 내역을 이미 연결을 유지하고 있는 ws로 보냄
- ws는 해당 이벤트를 위치 이동 이력 디비에 저장
- ws는 새 위치를 캐시에 보관, ttl 갱신
- 레디스 내의 해당 사용자 전용 채널에 새 위치를 발행, 3~5의 과정은 병렬로 진행
- 발행된 새 이벤트는 모든 구독자에게 브로드캐스드
- 받은 친구의 웹소켓 핸들러는 새 위치와 친구의 위치 사이 거리를 새로 계산한다. 검색 반경 내에 있다면 갱신 시각을 타임스탬프를 앱으로 전송하고 아니면 보내지 않는다.

Redis Pub/Sub(Publish-Subscribe)
Redis Pub/Sub은 실시간 메시징을 위한 Redis의 기능입니다. **발행자(Publisher)**가 메시지를 특정 채널에 발행하면, 해당 채널을 구독(Subscriber) 중인 모든 클라이언트에게 메시지가 전달됩니다.
작동 방식
- 채널 생성 및 구독: 구독자는 하나 이상의 채널에 구독 요청을 보냅니다.
- 메시지 발행: 발행자는 특정 채널에 메시지를 보냅니다.
- 메시지 전달: Redis는 메시지를 해당 채널에 구독 중인 모든 구독자에게 즉시 전송합니다.
Pub/Sub 특징
- 실시간 메시징: Redis는 메시지를 즉시 구독자에게 전달합니다.
- 단순 구조: 메시지를 직접 큐에 저장하지 않고 바로 전송합니다.
- 비동기 통신: 발행자는 구독자의 상태를 신경 쓸 필요가 없습니다.
- 패턴 구독 지원: 특정 패턴에 맞는 채널 이름을 구독할 수 있습니다.
제약 사항
- 메시지 내구성 없음: 메시지는 발행 시점에 구독자가 없으면 소멸됩니다.
- 확장성 제한: 수많은 구독자가 있는 경우 성능 저하 가능성
- 수평 확장 어려움(클러스터 모드에서 제한적)

Redis Pub/Sub 특징
- 메시지 휘발성: 구독자가 없으면 메시지는 즉시 소멸합니다.
- 빠른 실시간 통신: 짧은 수명의 이벤트나 알림에 적합합니다.
- 단순한 구조로 설정과 사용이 쉽습니다.
- 단점: 내구성 부족, 대규모 확장에 한계가 있음.
Kafka 특징
- 내구성 보장: 메시지를 디스크에 저장하여 장애 복구가 가능합니다.
- 확장성: 클러스터링으로 대량 데이터 처리가 가능합니다.
- 높은 안정성: 정확히 한 번 처리(Exactly Once Processing) 모델 지원.
- 적용 분야: 대규모 데이터 스트리밍, 로그 수집, 이벤트 중심 아키텍처에 적합.
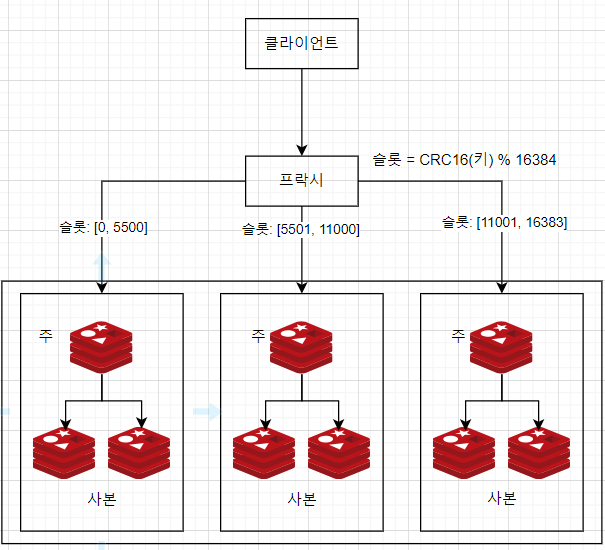
해시 링(Hash Ring)
1. 개념
일관성 해싱을 원형(topology) 구조로 시각화한 표현입니다. 해시 값을 0에서 최대값까지 원형 형태로 배치하고 노드와 데이터 키를 이 링 위에 매핑합니다. 해시 링(Hash Ring)은 데이터 분산 및 노드 추가/제거를 효율적으로 관리하기 위해 사용되는 분산 시스템 기법입니다. 데이터 노드를 원형(ring) 형태로 배치하고, 해싱을 통해 데이터를 특정 노드에 매핑합니다.
2. 동작 방식
- 모든 노드와 데이터 키에 대해 동일한 해시 함수(예: SHA-1)를 사용하여 해시 값을 계산합니다.
- 해시 값은 0부터 최대 값까지 이어지는 원형 공간(Ring) 상에 매핑됩니다.
- 데이터의 해시 값에 가장 가까운 시계 방향 노드가 해당 데이터를 담당합니다.
3. 해시 링의 특징
- 확장성: 노드를 추가하거나 제거할 때 전체 데이터 재배치 비용이 최소화됩니다.
- 부하 분산: 데이터가 노드에 고르게 분산됩니다.
- 내결함성: 특정 노드 장애 발생 시 데이터를 인접 노드로 쉽게 재분배합니다.
4. 장점
- 노드 추가/제거에 따른 재배치 비용 감소
기존 해싱 방식에서는 노드를 추가하면 모든 데이터의 재분배가 필요하지만, 해시 링에서는 평균적으로 전체 데이터의 1/n만 재분배됩니다. - 노드 장애 시 데이터 손실 최소화
특정 노드가 장애가 나더라도 인접 노드가 데이터를 처리하므로 손실이 줄어듭니다.
사용 사례
- 분산 캐시 시스템:
- Redis Cluster
- Memcached
- 분산 데이터 저장소:
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Apache Cassandra
- 분산 메시지 큐
- Kafka 파티션 데이터 분배
Consistent Hashing (일관성 해싱)
Consistent Hashing은 분산 시스템에서 데이터 분배와 부하 분산을 효율적으로 관리하기 위해 사용되는 해싱 기법입니다. 노드 추가/삭제 시 전체 데이터가 아닌 일부 데이터만 재배치되도록 하여 성능을 개선합니다.
작동 원리
- 해시 공간의 원형 구조 (Hash Ring)
- 해시 값이 0부터 최대값까지 연결된 원형 링 형태의 해시 공간을 형성합니다.
- 노드와 키의 매핑
- 각 노드(서버)는 해시 함수에 의해 링의 특정 위치에 할당됩니다.
- 각 데이터 키도 같은 해시 함수로 링 상에 위치합니다.
- 특정 키는 해시 링에서 **가장 가까운 노드(시계 방향)**에 할당됩니다.
- 노드 추가/삭제
- 기존 분배된 대부분의 키는 유지되며, 소수의 키만 재배치되므로 효율적입니다.


분산 레디스 펍섭 서버 클러스터
웹소켓 서버는 해시 링을 참조하여 메시지를 발행할 레디스 서버를 선정
웹소켓 서버는 해당 서버가 관리하는 사용자 채널에 위치 정보 변경 내역을 발행
레디스 펍섭서버는 각 채널의 구독자 목록을 들고 있기 때문에 유상태 서버. 제거 시 채널을 다른 서버로 옮기고 모든 구독자들에게 알려줘야 한다. 보통 유상태 서버 클러스터 규모를 늘리거나 줄이는 것은 큰 운영 부담으로 보통은 여유를 두고 오버 프로비저닝한다.
펍섭서버를 늘리면 대규모 채널 재조정(재구독)이 일어나기 때문에 CPU부하가 올라간다.
기존 서버를 교체하는 것은 채널 재조정 작업이 없기에 더 안전하다.. 교체하면 교체사실은 웹소켓 서버에게 통지되고 새 펍섭서버의 채널을 다시 구독하도록 알린다.
친구 추가 삭제 시: 친구의 펍섭 채널을 구독하거나 구독 취소한다.
친구가 많은 사용자? 친구에 상한선이 있고(5000명) 많은 웹소켓 서버에 분산되어 있으니 핫스팟 문제는 발생하지 않을 것..
주변의 임의의 사용자? 지오 해시별로 펍섭채널을 두어 사용자의 위치가 변경되면 지오해시 아이디를 계산한 후 해당 지오해시 아이디를 담당하는 채널에 새 위치를 전송한다. 근방에 있는 사용자 중 해당 채널을 구독하는 사용자2는 사용자의 위치가 변경되었다는 메시지를 수신한다.
얼랭으로 확장
웹소켓 서비스는 얼랭으로 구현하고 레디스 펍섭클러스터는 아예 분산 얼랭 애플리케이션으로 대체. 이 애플리케이션에서 각 사용자는 얼랭 프로세스로 표현. 이 사용자 프로세스는 클라이언트가 전송하는 갱신된 사용자 위치를 웹소켓 서버를 통해 수신. 또한 친구의 얼랭 프로세스와 구독 관계를 설정하고 변경 내역을 수신한다..
Erlang이란? 분산이 쉽고 경랑이라서 천만명의 활성 사용자 처리 굿,,
Erlang은 동시성(concurrency), 분산 시스템(distributed systems), 고가용성(high availability)을 위해 설계된 함수형 프로그래밍 언어이자 런타임 환경. 원래 스웨덴의 통신 회사 Ericsson에서 1986년에 통신 장비를 개발하기 위해 만들어졌으며, OTP(Open Telecom Platform)이라는 프레임워크와 함께 강력한 분산 시스템을 쉽게 구축할 수 있도록 지원
Erlang의 주요 특징
1. 동시성 (Concurrency)
- 수천만 개의 경량 프로세스(lightweight processes)를 동시에 관리
- 프로세스 간 비동기 메시지 전달 기반 아키텍처
- Actor Model 기반으로 상태 공유 없이 독립된 프로세스 실행
- Actor Model은 동시성(concurrency) 프로그래밍을 위한 추상화 모델입니다. 이 모델에서는 Actor(액터)가 기본 단위로 동작하며, 서로 독립적으로 실행되고 비동기 메시지 전달을 통해 통신합니다.
2. 고가용성 (High Availability)
- 핫 스왑(Hot Code Swapping) 지원: 실행 중인 시스템에서 코드 변경 가능
- 장애 복구 메커니즘: 프로세스가 실패하더라도 시스템 전체에 영향을 주지 않음
3. 분산 처리 (Distributed Systems)
- 여러 노드를 클러스터링하여 네트워크 기반 분산 시스템 지원
- 노드 간 메시지 전달과 동기화가 자동으로 이루어짐
4. 내장 장애 복구 (Fault Tolerance)
- 프로세스가 죽으면 이를 감시하는 Supervisor가 자동으로 복구
5. 함수형 프로그래밍 (Functional Programming)
- 부수 효과(Side Effect)를 줄이는 방식으로 오류를 예방
- 순수 함수(Pure Functions)와 패턴 매칭(Pattern Matching) 지원

'개발 > 도서 스터디' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [대규모 시스템 설계 기초2] 3장 구글맵(SSE, ws) (2) | 2025.02.02 |
|---|---|
| [대규모 시스템 설계 기초2] 1장 근접성 서비스(지오해시) (0) | 2025.01.31 |
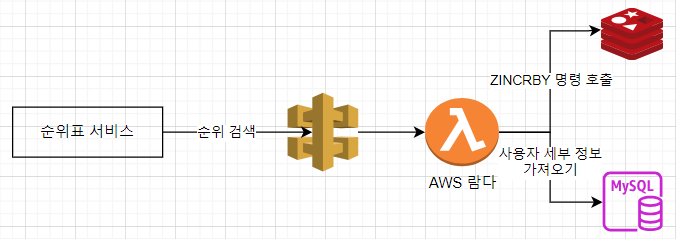
| [대규모 시스템 설계 기초2] 10장 실시간 게임 순위표(레디스, dynamo) (0) | 2025.01.29 |
| [대규모 시스템 설계 기초2] 9장 S3와 유사한 객체 저장소 (0) | 2025.01.28 |
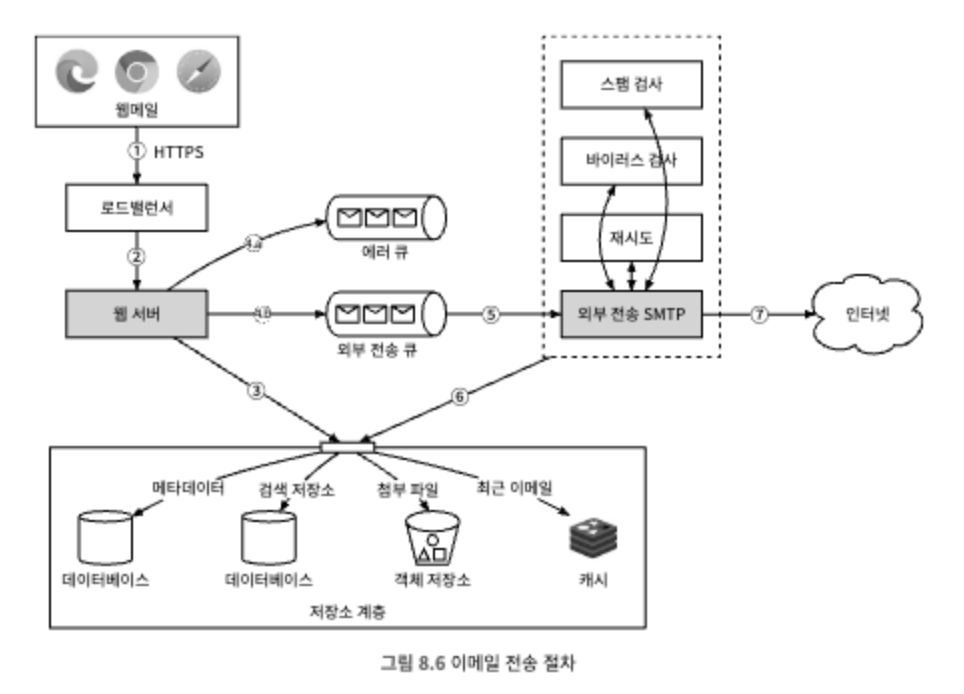
| [대규모 시스템 설계 기초2] 8장 분산 이메일 서비스 (0) | 2025.01.27 |