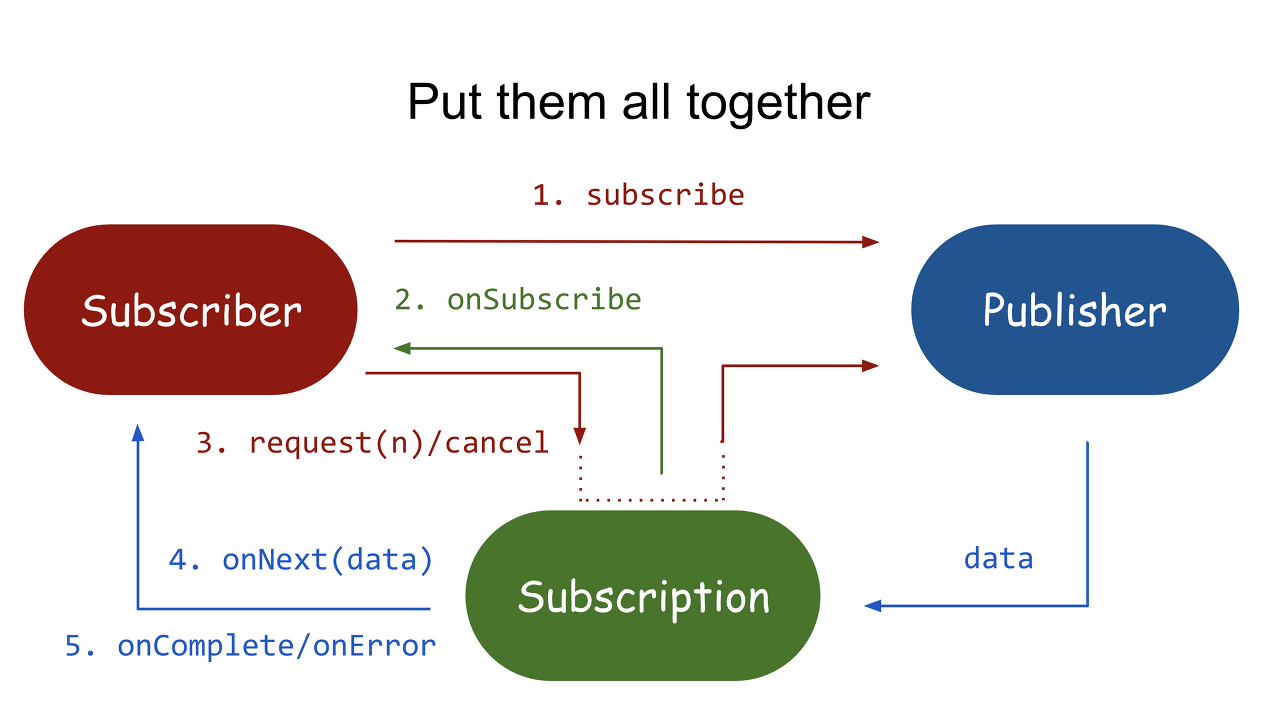
오늘은 5강을 이어서 학습한다.
1. default, blocking request
아래 그림처럼 2초씩 지연이 있는 /service를 요청하는 /rest를 100건 rest template로 요청한다. /rest의 스래드가 한 개라서 2초씩 대기한다.

@Slf4j
public class LoadTest {
static AtomicInteger cnt = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
RestTemplate rt = new RestTemplate();
String url = "http://localhost:8080/rest?idx={idx}";
CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(101);
for(int i = 0; i <100; i++){
es.submit(() -> {
int idx = cnt.addAndGet(1);
//blocking till await을 만난 숫자가 100에 도달할 때 까지 ; 그 순간에 블라킹이 한번에 풀려; 스레드 동기화 가능; 100개가 동시에 시작
//throw exception하기 때문에 callable 구현 필요
barrier.await();
log.info("thread {}", idx);
StopWatch s1 = new StopWatch();
s1.start();
String res = rt.getForObject(url, String.class, idx);
s1.stop();
log.info("elapsed:{} -> {} / {}", idx, s1.getTotalTimeSeconds(), res);
return null; //callable 구현한 인터페이스라고 생각함
});
}
barrier.await();
StopWatch sw = new StopWatch();
sw.start();
//graceful shutdown이라서 먼저 걸고 기다림
es.shutdown();
es.awaitTermination(100, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
sw.stop();
log.info("total time {}", sw.getTotalTimeSeconds());
}
}@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
@RestController
public static class MyController{
RestTemplate rt = new RestTemplate();
//thread 1개
//2초씩 대기; 톰캣 큐에 대기
@GetMapping("/rest")
public String rest(int idx){
//RestTemplate blocking; 응답올때까지 대기; 스레드가 더 필요로하는 요청이라면 홀딩
String res = rt.getForObject("http://localhost:8081/service?req={req}", String.class, "hello" + idx);
return res;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
//설정
server.tomcat.threads.max=1
spring.task.execution.pool.core-size=100@SpringBootApplication
public class RemoteService {
@RestController
public static class MyController{
@GetMapping("/service")
public String service(String req) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(2_000);
return req + "/service";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//application.properties 오버라이드하는 설정
System.setProperty("server.port", "8081");
System.setProperty("server.tomcat.threads.max", "1000");
SpringApplication.run(RemoteService.class, args);
}
}...
12:23:06.118 [pool-1-thread-39] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Reading to [java.lang.String] as "text/plain;charset=UTF-8"
12:23:06.119 [pool-1-thread-39] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:39 -> 8.463001595 / hello39/service
12:23:08.127 [pool-1-thread-30] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Response 200 OK
12:23:08.127 [pool-1-thread-30] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Reading to [java.lang.String] as "text/plain;charset=UTF-8"
12:23:08.127 [pool-1-thread-30] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:30 -> 10.472331585 / hello30/service
12:23:10.139 [pool-1-thread-34] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Response 200 OK
12:23:10.139 [pool-1-thread-34] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Reading to [java.lang.String] as "text/plain;charset=UTF-8"
12:23:10.140 [pool-1-thread-34] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:34 -> 12.485099461 / hello34/service
...2초 이상이 걸리는 100건의 작업이고 응답을 기다리는 동안은 블로킹되기 때문에 총 200초가량 소요된다. 허나 복잡한 로직도 아니고, 사실 cpu는 놀고 있을 것이다.. 이를 비동기로 바꿔보자.
2. AsyncRestTemplate(spring5.0/springboot2.0에서 deprecated)
위 소스에서 /rest의 rest template만 바꿔본다.
@RestController
public static class MyController{
AsyncRestTemplate rt = new AsyncRestTemplate();
//thread 1개
@GetMapping("/rest")
public ListenableFuture<ResponseEntity<String>> rest(int idx){
//호출을 비동기로; 바로 스레드 리턴, 응답이 오면 콜백은 스프링이 알아서; 응답이 오면 이 컨트롤러의 응답이라 생각하고 처리함; 콜백을 처리할 필요 없음
//비동기를 호출하기 위해 스래드를 백그라운드에 미리 만들어; 자바의 api를 사용해서; 겉으로는 한 스레드에서 처리한 것 처럼 보이지만 사실 서버의 자원을 사용한 것
ListenableFuture<ResponseEntity<String>> res = rt.getForEntity("http://localhost:8081/service?req={req}", String.class, "hello" + idx);
return res;
}
}...
12:42:49.442 [pool-1-thread-54] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:54 -> 2.516070823 / hello54/service
12:42:49.444 [pool-1-thread-98] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Response 200 OK
12:42:49.444 [pool-1-thread-12] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:12 -> 2.513689601 / hello12/service
12:42:49.444 [pool-1-thread-98] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Reading to [java.lang.String] as "text/plain;charset=UTF-8"
12:42:49.445 [pool-1-thread-89] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Response 200 OK
12:42:49.445 [pool-1-thread-89] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Reading to [java.lang.String] as "text/plain;charset=UTF-8"
12:42:49.445 [pool-1-thread-98] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:98 -> 2.518126106 / hello98/service
12:42:49.445 [pool-1-thread-89] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:89 -> 2.515622072 / hello89/service
12:42:49.446 [main] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - total time 2.527531376이렇게 실행하면 총 실행시간이 2초 남짓으로 마치 요청 한 건을 한 것과 비슷하게 나온다. 하지만 자바에서 제공하는 분석 툴인 jmc를 이용하여 /rest를 실행한 애플리케이션의 thread의 개수를 확인해보면..

서블랫 스래드는 하나만 만들어져야 하는데, 사실 뒤에서는 100개 이상의 스레드를 추가적으로 생성해서 요청하고 있음을 알 수 있다. 톰캣이 100개의 스레드를 만들었나 싶은데, 사실 톰캣 스래드는 사진에서 보는 것과 같이 하나고, 자바 api를 통해 백그라운드에서 100개 스레드를 만들어 놓고 실행하는 것이다. 즉 매번 서버 자원을 사용한다는 것인데, 이는 비효율적이다. 최소한의 자원을 사용해야 한다.
3. netty / nonblocking io를 사용하는 client lib 사용
/rest 부분의 rest template를 async rest template으로 변경하고 네티를 사용한다. 네티의 스레드를 1개로 설정한다.
@RestController
public static class MyController{
//Netty4ClientHttpRequestFactory spring 제공
//netty도 스레드 1개
AsyncRestTemplate rt = new AsyncRestTemplate(new Netty4ClientHttpRequestFactory(new NioEventLoopGroup(1)));
//thread 1개
@GetMapping("/rest")
public ListenableFuture<ResponseEntity<String>> rest(int idx) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
log.info("/rest {}", idx);
//호출을 비동기로; 바로 스레드 리턴, 응답이 오면 콜백은 스프링이 알아서; 응답이 오면 이 컨트롤러의 응답이라 생각하고 처리함; 콜백을 처리할 필요 없음
//비동기를 호출하기 위해 스래드를 백그라운드에 미리 만들어; 자바의 api를 사용해서; 겉으로는 한 스레드에서 처리한 것 처럼 보이지만 사실 서버의 자원을 사용한 것
ListenableFuture<ResponseEntity<String>> res = rt.getForEntity("http://localhost:8081/service?req={req}", String.class, "hello" + idx);
return res;
}
}그리고 실행을 하면 처음에는 3초가 걸리고, 다시 또 실행을 하면.. 8초가 걸리고.. 다시 실행하면 timeout이 난다..
토비님과는 다른 결과.. 왜지ㅠ
...
15:13:45.147 [pool-1-thread-64] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:64 -> 3.230518378 / hello64/service
15:13:45.148 [pool-1-thread-82] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:82 -> 3.229926106 / hello82/service
15:13:45.148 [pool-1-thread-53] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:53 -> 3.229702047 / hello53/service
15:13:45.148 [pool-1-thread-62] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:62 -> 3.229505908 / hello62/service
15:13:45.149 [main] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - total time 3.242286844
...
15:15:27.268 [pool-1-thread-60] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - elapsed:60 -> 8.542415481 / hello60/service
15:15:27.268 [main] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - total time 8.556960287
...
15:18:02.122 [pool-1-thread-26] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Response 503 SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE
15:18:02.124 [pool-1-thread-18] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Response 503 SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE
15:18:02.124 [pool-1-thread-3] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Response 503 SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE
15:18:02.126 [pool-1-thread-12] DEBUG org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate - Response 503 SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE
15:18:02.129 [main] INFO toby.live.lecture4.LoadTest - total time 30.97585281
타임아웃이 나는 현상을 지켜보니 아래와 같은 순서로 진행되었다.
- LoadTest -> /rest로 100건 요청
- /rest에서 100건 요청받고 -> /service로 요청해야 하는데 /service 쪽 로그에 아무것도 안 찍힘
- 1분 뒤에 /rest에서 async request timeout exception 걸려서 503 return
- 그 후에 /service가 요청을 받아서 처리 하지만 /rest에서는 이미 exception 처리돼서 무쓸모
왜 /rest는 요청을 바로 받는데 /service로 바로 안 보내고 1분 후에 한 번에 보내는 걸까.. block 되어 있는 건가..
/rest가 1개의 스레드에서 도는데 어디선가 블라킹이 있어서 안 되는 것 같은데, 왠지 모르겠다. 느낌은 저 시대와 지금의 기본적인 풀 세팅 정보가 달라서 그럴 것 같다.
어쨌건 스레드를 100개씩이나 더 생성하지 않는 것은 확인했다.
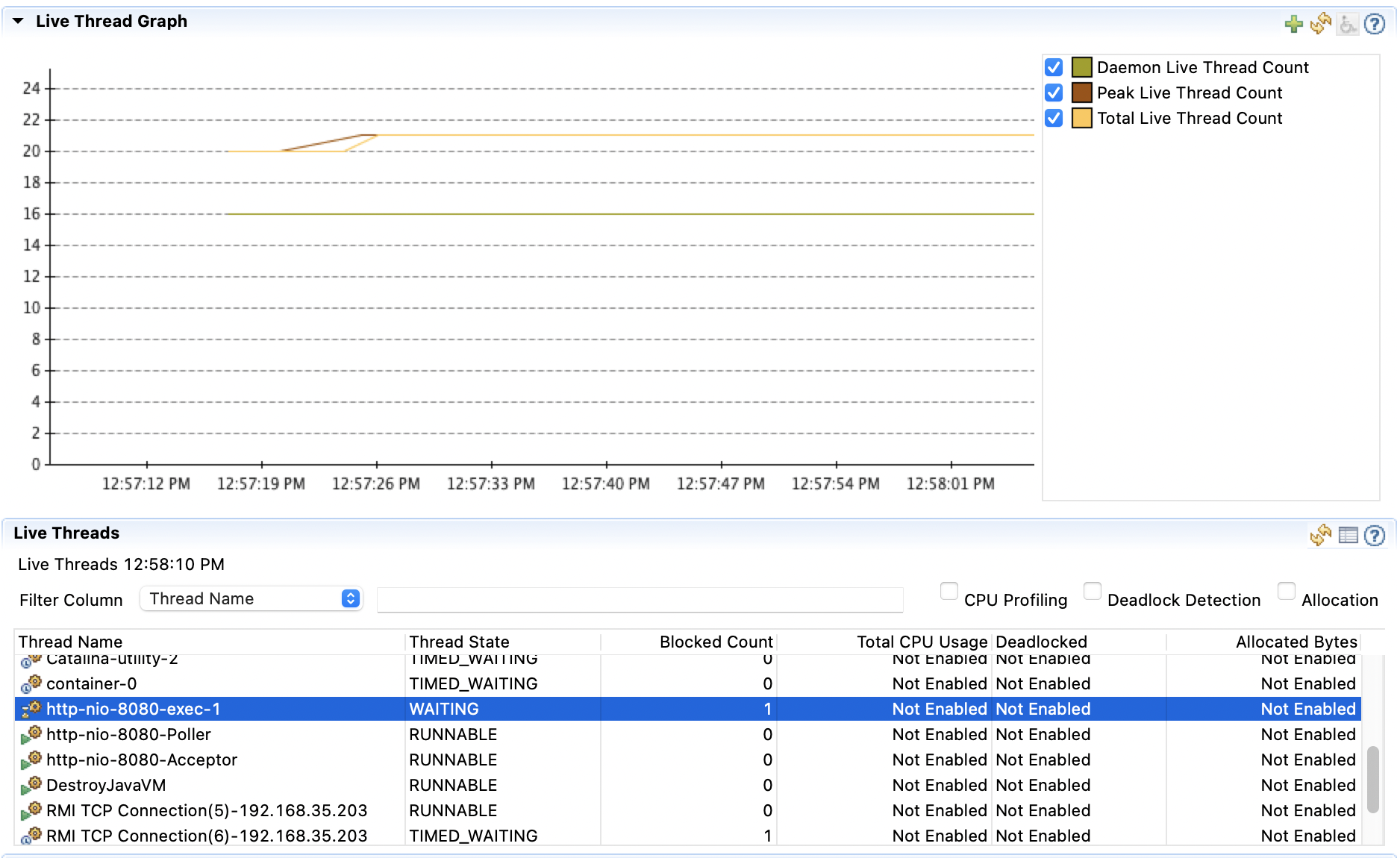
자꾸 타임아웃이 나지만 우선은 진행한다.
ListenableFuture로 응답을 그대로 내리면 응답을 꺼내서 수정할 수가 없다. 이때 사용 가능한 것이 DeferredResult이다.
ListenableFuture에 콜백을 달고 DeferredResult에 setResult를 하면 응답을 수정할 수 있다
@GetMapping("/rest")
public DeferredResult<String> rest(int idx) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
log.info("/rest {}", idx);
DeferredResult<String> dr= new DeferredResult<>();
ListenableFuture<ResponseEntity<String>> res = rt.getForEntity("http://localhost:8081/service?req={req}", String.class, "hello" + idx);
//res.get -> blocking 으로 바뀌어버림 의미없음
//callback이 실행되는거지 리턴을 주는게 아님; 응답을 받고 변형하려면? deferredReuslt!
res.addCallback(s -> {
dr.setResult(s.getBody() + "/work"); //응답 변형
}, e-> {
//throw 하면 어디서 에러가 난지 알 수 없어 비동기라
dr.setErrorResult(e.getMessage());
});
return dr;
}중첩 콜을 원한다면..
@GetMapping("/rest")
public DeferredResult<String> rest(int idx) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
log.info("/rest {}", idx);
DeferredResult<String> dr= new DeferredResult<>();
ListenableFuture<ResponseEntity<String>> res = rt.getForEntity("http://localhost:8081/service?req={req}", String.class, "hello" + idx);
res.addCallback(s -> {
ListenableFuture<ResponseEntity<String>> f2 = rt.getForEntity("http://localhost:8081/service2?req={req}", String.class, s.getBody());
f2.addCallback(s2-> {
dr.setResult(s2.getBody());
}, e2-> {
dr.setErrorResult(e2.getMessage());
});
}, e-> {
//throw 하면 어디서 에러가 난지 알 수 없어 비동기라
dr.setErrorResult(e.getMessage());
});
return dr;
}2초짜리 콜을 2번 중첩해서(/service2는 /service의 카피본이다) 4초가량이 걸린다. (하지만 역시 나는 위와 같은 현상이 계속되어서 안되었다..)
3번 중첩한다면..
@Slf4j
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
@RestController
public static class MyController{
//Netty4ClientHttpRequestFactory spring 제공
//netty도 스레드 1개
AsyncRestTemplate rt = new AsyncRestTemplate(new Netty4ClientHttpRequestFactory(new NioEventLoopGroup(1)));
@Autowired
MyService myService;
static final String URL1 = "http://localhost:8081/service?req={req}";
static final String URL2 = "http://localhost:8081/service2?req={req}";
//thread 1개
@GetMapping("/rest")
public DeferredResult<String> rest(int idx) {
log.info("/rest {}", idx);
DeferredResult<String> dr= new DeferredResult<>();
ListenableFuture<ResponseEntity<String>> f1 = rt.getForEntity(URL1, String.class, "f1" + idx);
f1.addCallback(s -> {
ListenableFuture<ResponseEntity<String>> f2 = rt.getForEntity(URL2, String.class, s.getBody());
f2.addCallback(s2 -> {
ListenableFuture<String> f3 = myService.work(s2.getBody());
f3.addCallback(s3 -> {
dr.setResult(s3);
}, e3 -> {
dr.setErrorResult(e3.getMessage());
}
);
}, e2-> {
dr.setErrorResult(e2.getMessage());
});
}, e-> {
dr.setErrorResult(e.getMessage());
});
return dr;
}
}
@Service
public static class MyService{
@Async
public ListenableFuture<String> work(String req){
return new AsyncResult<String>(req + "/asyncwork");
}
}
@Bean
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor myPool(){
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor te = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
te.setCorePoolSize(1);
te.setMaxPoolSize(1); //queue까지 다 차면 맥스
te.initialize();
return te;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}주의해야 하는 것은 어디서든 다 async, 비동기가 되게끔 작성해야 한다는 것, 아니면 순식간에 동기로 바뀐다.
'개발 > reactive' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [reactive] 7. CompletableFuture (0) | 2022.03.21 |
|---|---|
| [reactive] 6. refactoring (0) | 2022.03.21 |
| [reactive] 4-2. spring 비동기를 위한 interfaces/classes (0) | 2022.03.17 |
| [reactive] 4-1. java Future/FutureTask/Callable/Runnable (3) | 2022.03.16 |
| [reactive] 3. reactive streams - schedulers (1) | 2022.03.03 |